This week we are going to talk about problems with subject-verb agreement. Basically, subjects and verbs must agree in number. If the subject is plural, its verb also must be plural. For example, you would not say, “The dog are friendly” because the subject dog is singular and the verb are is plural. The sentence should, of course, be, “The dog is friendly.”
This is an easy example. But subject-verb agreement gets much more difficult, especially in sentences with complex subjects or when the subject is separated from its verb.
Compound subjects
Let’s start with compound subjects. A compound subject is two or more individual nouns connected into a larger noun phrase. For example, “Sherry and her friends from Florida are coming to visit.” The key word here is and. “Sherry and her friends from Florida” is the compound subject. When you have two or more subjects connected by and, use a plural verb. “Salt and pepper are popular condiments.” However, if you have two singular subjects connected by the word or, use a singular verb. For example, “My mother or my father drives me to school every day.”
Gerund subjects
Now let’s look at gerunds. A gerund is the –ing form of a verb that acts as a noun. Gerund subjects are singular. For example, “Running is fun.” The gerund is running. A longer gerund phrase is still singular, even if the phrase ends with a plural noun. For example, “Running with my friends is fun.” You can learn more about gerunds in our episode on gerunds and infinitives.
Group nouns
Group nouns, also called collective nouns, can also be confusing. These are nouns like committee, staff, family, and crew. Group nouns suggest more than one person, but they are still singular for grammatical purposes, such as, “My family is here” or “The new staff starts tomorrow.”
Americans use a singular verb after a group noun. The British, on the other hand, use both singular and plural verbs after group nouns. So, you might hear someone from the UK say, “The team are winning” or “The team is winning.”
Country names
Country names, even if they end in –s, are still singular. For example, “The Philippines is a country in Asia.” However, if you are speaking about people of the country, use the plural. For example, “The Filipinos are friendly.”
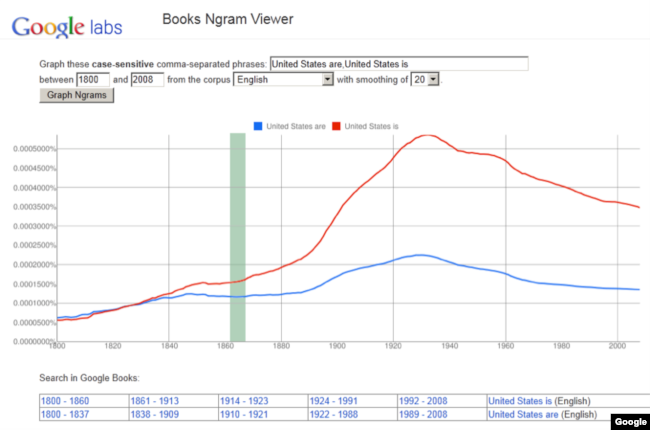
The United States is a singular noun. But this was not always true. Before the American Civil War in the 1860s, many people said, “The United States are,” instead of “The United States is”.
Civil War historian Shelby Foote said the change from are to is shows a change in American thinking. Before the Civil War, many people thought of the United States as a collection of independent states. After the Civil War, more Americans thought of themselves as a single country. As Mr. Foote famously said, the Civil War “made us an is.”
Words that are always singular
Some common adjectives and pronouns are always singular. Indefinite pronouns ending in –body, -one, and –thing are never plural. For example, “Everyone who drives to work faces heavy traffic.”
Distributive words like each and every are always singular. For example, “Every student and teacher works very hard.” Even though there are two nouns connected by and, the verb is still singular following every.
Each and every often confuse even native English speakers. For this reason, they are a popular topic for makers of standardized tests like the SAT. For example, “Each of the boys has his own book.” A lot of Americans would say, “Each of the boys have their own book.” Both ways are acceptable in everyday conversation. But in formal writing and standardized tests, the first sentence is more correct: each makes the sentence singular, regardless of what follows it. For more on this topic, see our episode, Problems with Pronouns and Gender.
Test maker tricks
Test makers often create trick questions by separating the subject and the verb, hoping to mislead test takers into choosing the wrong answer.
Here is a rather extreme example of subject-verb separation: “Everybody who has ever gone on vacation to Indonesia or the Philippines knows that the water there is warm.” In this sentence the subject everyone is separated from the main verb knows by a long subordinate clause. But the rule is the same: every makes the subject singular, no matter how far away the main verb may be.
Also, be careful with the word none. In very formal grammar, none is a contraction for the singular not one. It is common to use none with both singular and plural verbs. You will hear, “None of you are listening” and “None of you is listening.” But in very formal grammar, none is only used with singular verbs.
Words that are always plural
There are a few English words that are always plural. The most common ones are glasses (when referring to eye glasses), trousers, pants, scissors, clothes and police. In addition, the names of some academics subjects are always plural such as physics, mathematics, and economics.
The bottom line
Subject-verb agreement is the foundation of grammar. The most important thing to remember is this: subjects and verbs are sometimes separated. Don’t examine grammar with tunnel vision. Slow down, step back and look at the whole sentence in context.
I’m Jonathan Evans.
Text Source: VOA. “Everyday Grammar: Understanding Subject-Verb Agreement.” VOA, VOA - Voice of America English News, 25 Sept. 2015, learningenglish.voanews.com/a/everyday-grammar-do-does-you-understand-subject-verb-agreement/2977592.html. Accessed 9 Dec. 2019.
Lessons and Exercises:
- BBC Masterclass: Subject-Verb Agreement
- BBC Masterclass: Subject-Verb Agreement 1 (YouTube Video)
- BBC Masterclass: Subject Verb Agreement 2 (YouTube Video)
- BBC Masterclass: Subject Verb Agreement 3 (YouTube Video)
- GrammarBook.com
- Subject-Verb Agreement | Grammar Rules
- Subject and Verb Agreement Quiz 1
- Subject and Verb Agreement Quiz 2
- Purdue Online Writing Lab
- Towson University
- Subject - Verb Agreement - Exercise 1
- Subject - Verb Agreement - Exercise 2
- Subject - Verb Agreement - Exercise 3
- University of Victoria English Language Centre
Comments
Post a Comment